Casting Aluminum for various industries
top choice for creating lightweight, high-strength components with complex designs
Casting aluminium is a manufacturing process that creates aluminium parts by shaping molten aluminium. It allows for producing complex shapes and components with high dimensional accuracy and surface finish, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, and consumer goods.
Patternmaking/Preparation
The first step involves creating a pattern, a replica of the desired final aluminum part. Depending on the complexity, production volume, and cost considerations, this pattern can be made from various materials like wood, plastic, metal, or even 3D-printed.
Die Casting: A permanent steel mold, a die, is machined with the desired part cavity. This method is suitable for high-volume production.
The Aluminum Casting Process
Mold Preparation:
A mold cavity is created, usually made of steel or another heat-resistant material. This cavity replicates the desired final shape of the aluminum part. Depending on the complexity of the design, there can be one or two pieces.
Aluminum Melting:
Aluminum ingots or scrap are melted in a furnace at high temperatures (around 600-700°C).
Pouring the Molten Metal:
The molten aluminum is carefully poured or injected into the mold cavity. Different casting techniques use different pouring methods.
Solidification:
The aluminum is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold cavity, taking the shape of the cavity.
Part Removal and Finishing:
Once solidified, the mold is opened, and the cast aluminum part is removed. The part may undergo trimming, machining, or finishing to achieve the desired final dimensions and surface quality.
Benefits of Casting Aluminum:
Complex Shapes: Casting allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes that would be difficult or expensive to produce with other methods like machining.
Lightweight Parts: Aluminum is a lightweight metal, making cast aluminum parts ideal for applications where weight reduction is important (e.g., aerospace, automotive).
Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio: While lightweight, cast aluminum offers good mechanical strength and rigidity.
Mass Production: Casting is suitable for mass production of highly consistent identical parts.
Recyclable: Aluminum is a highly recyclable material, making casting an eco-friendly option in many cases.
Types of Aluminum Casting:
There are various casting techniques used for aluminum, each with its own advantages and limitations. There are several methods of casting aluminum, each suited to different types of products and production volumes.
- Sand Casting: Molten aluminum is poured into a mold made of sand. This is one of the oldest and most versatile methods, ideal for producing large parts or small production runs.
- Die Casting: Molten aluminum is injected under high pressure into steel molds (dies). This process allows for high-volume production of complex shape parts with excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances.
- Permanent Mold Casting: Molten aluminum is poured into a reusable metal mold, producing stronger parts with a better surface finish than sand casting.
- Investment Casting (Lost-Wax Casting): A wax pattern is coated with ceramic, melted out, and molten aluminum is poured into the mold, allowing for the creation of highly detailed parts with excellent surface finish.
- Centrifugal Casting: Molten aluminum is poured into a rotating mold, which forces the metal outward to create cylindrical parts, often used for pipes and rings.
The choice of casting method depends on factors like the part geometry, production volume, required tolerances, and cost considerations.
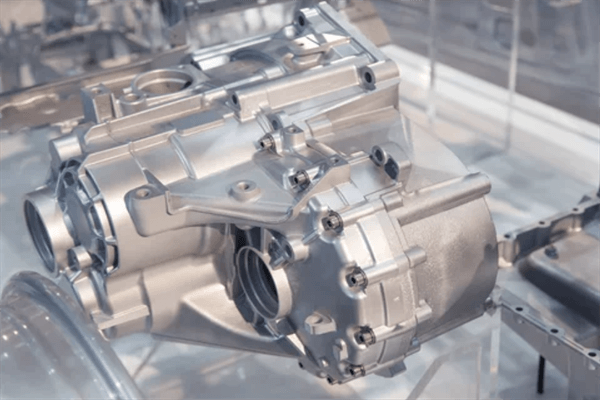
Applications of Cast Aluminum:
Cast aluminum finds applications in a wide range of industries due to its versatility and combination of properties:
Automotive: Engine components (blocks, heads, pistons), wheels, transmission housings
Aerospace: Aircraft parts, spacecraft components requiring lightweight and high-strength materials.
Construction: Building components like window frames, brackets, decorative elements.
Consumer Goods: Furniture parts, appliance housings, electronic equipment chassis, sporting goods.
Industrial Machinery: Machine parts, pumps, valves, housings for various industrial equipment.
How to Choose the Right Aluminum Casting Process?
Selecting the most suitable aluminum casting process for your project requires careful consideration of several factors. Each method—whether sand casting, die casting, or permanent mold casting—offers unique advantages that can impact the outcome of your final product. Here’s how to determine the right process for your needs:
1. Design Complexity
The complexity of your design plays a significant role in choosing a casting method. For larger and intricate designs, sand casting is often the go-to choice, as it easily accommodates complex shapes and structures. If your aluminum part demands higher dimensional accuracy, permanent mold casting is a better fit, providing precision without sacrificing quality.
2. Speed of Production
When speed is a critical factor, die casting stands out. This process uses pressurized injection to form parts, making it the fastest method for mass production. Sand casting follows in terms of speed, while permanent mold casting takes longer but may offer superior accuracy for smaller batches.
3. High-Volume Production
For large-scale manufacturing, die casting is the most effective solution due to its ability to produce a high number of consistent aluminum parts in a short time. If you’re looking for a compromise between volume and tooling costs, sand casting and permanent mold casting offer a balance. These methods work well for medium to high production runs without the high cost associated with die casting tools.
4. Prototyping
When prototyping or producing small quantities, sand casting is ideal. The initial tooling and setup costs are minimal, making it the most cost-effective choice for prototypes. In contrast, die casting and permanent mold casting require more upfront investment, making them less suitable for projects requiring only a few pieces.
5. Strength and Surface Finish
For projects requiring a strong final product with a smooth surface, permanent mold casting is often the best choice. This method balances strength with a high-quality finish. Die casting also produces parts with excellent surface finishes but may not achieve the same strength as permanent mold castings. Meanwhile, sand casting delivers robust components but with a rougher finish, often requiring secondary processing for a smoother appearance.
By understanding these factors—design complexity, production speed, quantity, prototyping needs, and surface finishing—you can better determine which aluminum casting process is right for your project. Each method has its strengths, and making the right choice will ensure your casting delivers both in quality and cost-effectiveness.
Expert Aluminum Casting Solutions
Unlock the potential of aluminum casting for your business! Whether you need lightweight, high-strength components or intricate designs, our expert casting solutions can meet your exact specifications. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how aluminum casting can enhance your production efficiency and product performance.
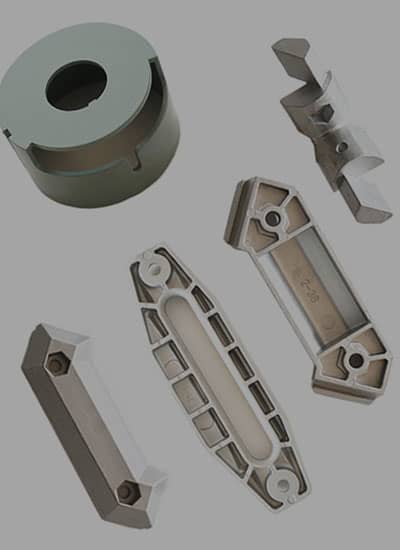
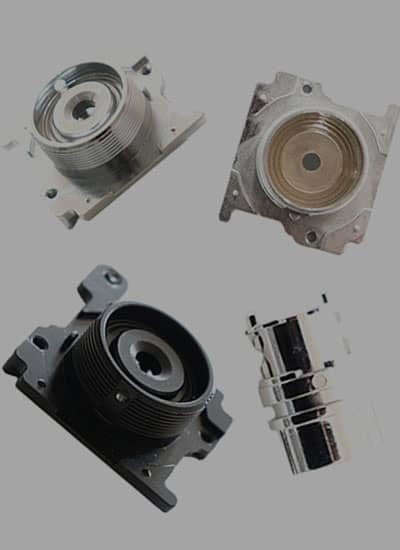
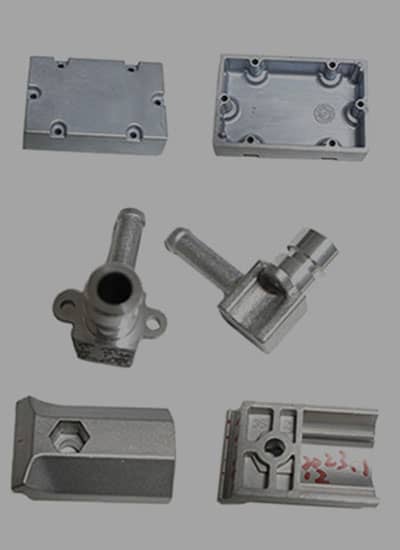













No comment