Quality Control in Aluminum Die Casting
Ensuring quality assurance is paramount in die casting processes. Hence, comprehensive die casting product testing and quality control measures are imperative to ascertain defect-free products that adhere to requisite standards. Various tests and procedures are employed to evaluate the quality of die castings, encompassing dimensional tolerances, mechanical testing, visual inspection, and additional assessments. By upholding these rigorous quality standards, companies preempt costly recalls and mitigate the risk of customer dissatisfaction, thereby upholding their reputation for excellence and reliability in the market.
Key points in die casting quality control:
- Mold design and maintenance.
- Process control.
- Material quality.
- Operator training.
- Inspection and testing.
- Continuous improvement.
Tooling Design for aluminum casting die.
High-quality molds are essential for producing accurate and defect-free parts. Proper mold design and regular maintenance ensure consistent part quality and minimize defects.
Software in Design:
- CAD/CAM Software: Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software design die casting molds and simulate the die casting process. This software helps create precise 3D models of parts, optimize mold designs, and simulate the flow of molten metal to identify potential defects.
- Simulation Software: Die casting simulation software predicts potential defects such as porosity, shrinkage, and air entrapment in the casting process. It helps in optimizing process parameters to improve casting quality and reduce defects.
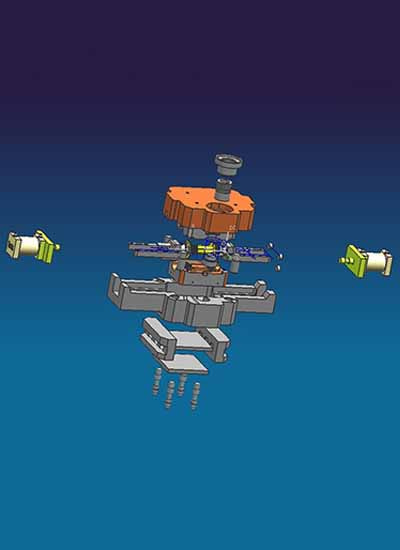
Casting Geometry: The design of the casting geometry determines the shape, size, and features of the final aluminum part. It includes draft angles, fillets, ribs, and surface finishes to facilitate smooth metal flow and part ejection.
Parting Line: The parting line separates the mold into two halves (core and cavity) and dictates how the mold will split for part ejection. Its location is carefully chosen to minimize flash and streamline mold assembly and disassembly.
Process Control In Die Casting
Process control in die casting is essential for ensuring the quality and consistency of cast parts.
Temperature Control: Maintaining proper temperature control is critical for achieving optimal casting quality. This includes controlling the temperature of the molten metal, die temperature, and the temperature of the various components of the die casting machine. Temperature monitoring and regulation help prevent issues such as premature solidification, porosity, and shrinkage defects.
Pressure Control: Proper pressure control is necessary to ensure the complete filling of the die cavity and the formation of high-quality castings. The injection pressure, holding pressure, and intensification pressure need to be carefully controlled and adjusted based on factors such as part geometry, material properties, and casting cycle parameters.
Injection Speed and Timing: Controlling the injection speed and timing is crucial for achieving uniform filling of the die cavity and minimizing defects such as cold shuts, flash, and air entrapment. Adjusting the injection speed and timing based on the part design and material properties helps optimize the casting process and improve overall quality.
Inspection and Testing
Comprehensive inspection and testing procedures, including dimensional measurement, visual inspection, non-destructive testing, and mechanical testing, help identify defects and ensure compliance with specifications and standards.
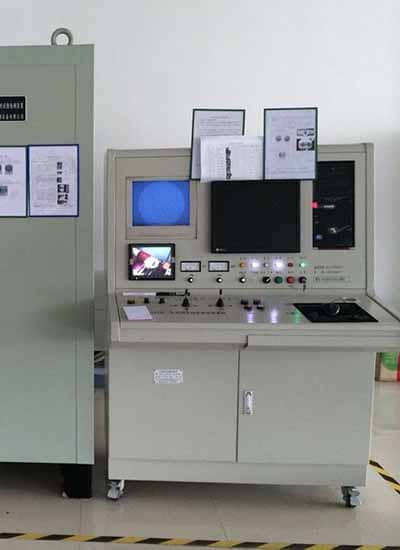
X-ray Inspection
X-ray and CT Scanning: X-ray and CT scanning are used for non-destructive inspection of internal features and defects in die cast parts. They can detect casting porosity, inclusions, and other internal defects without damaging the parts.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Another NDT technique, UT, is used to detect subsurface defects in castings. It offers real-time feedback, allowing manufacturers to identify flaws early in production.

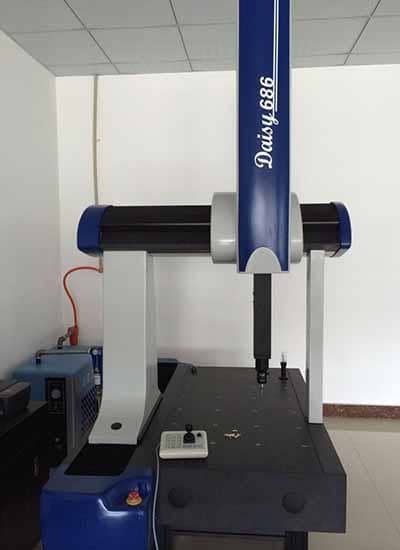
Dimensional Accuracy
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM): A CMM accurately measures the dimensions and geometry of die cast parts. It can verify the dimensional accuracy of critical features and ensure compliance with specifications.
- Optical Comparator: An optical comparator performs non-contact measurements of complex shapes and contours. It provides high magnification and precise measurements for detailed inspection of die cast parts.

By implementing these detailed quality control measures, DSW die-casting manufacturers can ensure that their products consistently meet the highest quality standards, resulting in customer satisfaction, improved reliability, and compliance with industry regulations.










No comment