
Comprehensive Guide to Assembly Methods for Die-Cast Parts
Die casting has emerged as a cornerstone of modern metalworking, renowned for its ability to produce high-quality, intricate parts in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and surface finishes. This versatility extends beyond the initial casting process, as die-cast components often require assembly to realize their full functionality. Selecting the optimal assembly method holds significant influence on the final product’s performance, cost-effectiveness, and overall production efficiency.
This comprehensive guide delves into the most prevalent assembly techniques employed for die-cast parts, meticulously outlining their advantages, limitations, and ideal applications. By equipping you with a thorough understanding of these methods, we empower you to make informed decisions that optimize your die-cast assembly process.
Joining Components with Die Casting Assembly
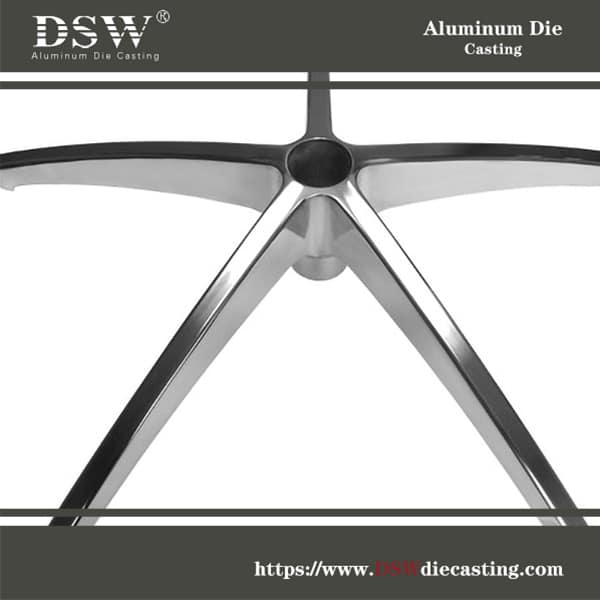
Die casting assembly is an essential method for bringing together components across a variety of industries, especially in the realm of appliance manufacturing. This technique is widely used to connect an array of parts, including abrasive wheels, discs, electric motor rotors, gears, magnets, cups, and more, to posts, stems, shafts, and mandrels crafted from almost any material you can think of.
Imagine the intricate dance of these components as they come together, forming a cohesive unit ready to perform its task. Die casting allows for a seamless integration, ensuring that each part fits perfectly and works harmoniously with the others.
Exploring the Spectrum of Assembly Methods:
1. Adhesive Bonding:
This method utilizes specialized adhesives to create a strong, versatile joint between die-cast components. While offering benefits like sealing, insulation, and corrosion resistance, it may not suit applications experiencing high stress levels. Additionally, thermal degradation and peeling can pose challenges in specific scenarios.
.
2. Attachment Systems:
Tailored for high-ductility alloys like zinc, attachment systems utilize techniques like crimping, staking, and swaging to achieve permanent bonds. These techniques offer a more uniform stress distribution than adhesives and are often favoured for their speed of implementation.
3.External Threads:
Die-cast parts can be designed to incorporate external threads, enabling efficient assembly through bolts and nuts. This widely adopted approach necessitates carefully considering flash removal, which can be generated during the casting process at thread intersections.
4. Forming or Self-Cutting Fasteners:
This method leverages hard steel fasteners that embed themselves within the die-cast material during installation. Self-tapping and thread-forming screws are prominent examples, offering a robust and secure hold in softer die-cast alloys. However, this technique might generate small metal chips that could pose issues in sensitive electronic applications.
5.Injected Metal Assembly (IMA):
Similar to adhesive bonding, IMA employs molten metal as the joining agent. This method creates a robust, permanent mechanical lock capable of withstanding significant loads and bonding dissimilar materials (metals to non-metals).
6. Inserts:
When the intended application demands exceptional strength or the die-cast material exhibits limitations, inserts become the preferred choice. These pre-fabricated components, cast-in-place or post-installed, offer enhanced load-bearing capabilities and resistance to wear and tear.

7.Interference Fits:
This technique relies on a slight dimensional difference between mating parts to create a tight, secure joint. While offering a simple and cost-effective approach, interference fits require meticulous design and fabrication to ensure proper assembly and avoid part damage.
8. Threaded Fasteners:
Threaded fasteners are a mainstay in assembly practices. They utilize bolts, nuts, and tapped holes to join die-cast components. This traditional method offers a high degree of adjustability and ease of disassembly, making it ideal for applications requiring future maintenance or access. Considering the die-cast material’s strength and design bosses with sufficient diameter to accommodate the chosen threads is crucial.
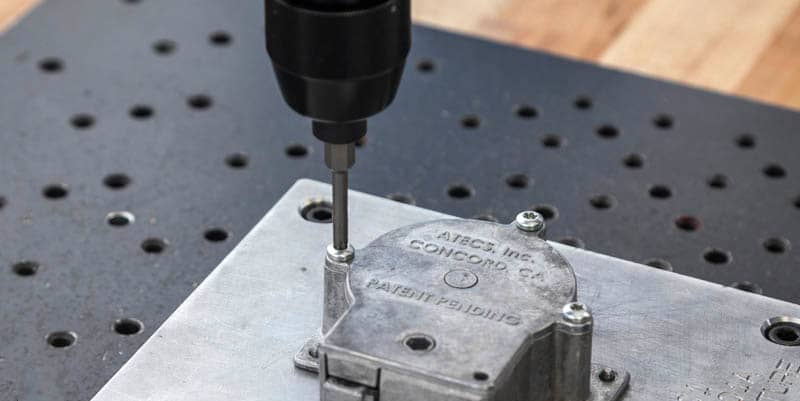

Optimizing Your Assembly Process:
The ideal assembly method hinges on a nuanced understanding of various factors impacting your project. These considerations include:
- Strength Requirements: The anticipated loads and stresses the assembled product will encounter.
- Material Selection: The properties of the chosen die-cast alloy and any potential compatibility issues with the joining method.
- Part Geometry: The design complexity of the parts and how it influences assembly feasibility.
- Cost and Production Speed: Balancing cost-effectiveness with the desired production timeline.
In essence, die casting assembly not only enhances the performance of individual parts but also elevates the functionality of the final product. It’s a technique that combines precision and reliability, making it indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Casting Assembly Solutions from DSW
DSW, a leading manufacturer with extensive experience in die casting, possesses the expertise to guide you through the intricate world of assembly methods. Our team of dedicated engineers can help you navigate every stage, from material selection and design optimization to the implementation of the most suitable assembly approach.
By leveraging DSW’s comprehensive knowledge and commitment to quality, you gain the confidence and expertise to create high-performance die-cast assemblies that deliver exceptional value and exceed expectations.









No comment