In a world where precision and efficiency are paramount, zinc casting molds stand out as a revolutionary technology transforming manufacturing. By offering unparalleled accuracy and versatility, these molds are essential for achieving high-quality results across various industries. In this article, we delve into the incredible benefits of zinc casting molds, exploring how they drive success in automotive, electronics, aerospace, and beyond.
Zinc Casting Molds in Achieving High-Quality Manufacturing
Achieving exceptional quality in the ever-changing landscape of manufacturing is a constant quest. Zinc molds are a crucial advancement in this quest. They deliver unparalleled precision and efficiency to various industries. This article examines the impact of zinc-casting moulds on multiple industries, from their technical characteristics to their wide range of applications. It also highlights their contribution to quality results.

What Are Zinc Casting Moulds?
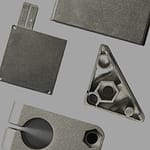
Zinc casting moulds, utilised in zinc alloy die casting, involve injecting molten zinc under high pressure into precision-engineered steel dies. The rapid cooling and solidification result in short production cycles and minimal material waste. This process enables manufacturers to produce complex, high-quality parts consistently and efficiently.
Key Advantages:
- High Precision: Zinc Die Casting Molds enable the creation of intricate components with tight tolerances, essential for industries requiring exact specifications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The speed of production and minimal waste make zinc alloy die casting a cost-effective solution for large-scale operations.
- Enhanced Performance: Industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace benefit from the strength, lightweight properties, and superior surface finishes of zinc-cast components.
Industry Applications
Zinc Casting Molds in Various Industries
Automotive: Zinc die casting molds are widely used in the automotive industry to produce lightweight yet robust components. These parts contribute to improved vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
Electronics: Zinc alloy molds are used to produce small, intricate components with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. These molds are ideal for electronic components, connectors, heat sinks, and other electronic components.
Aerospace: The aerospace industry demands components that are lightweight, strong, and reliable. Zinc alloy die casting molds are used to produce precision aerospace components, improving flight safety and fuel economy.
Consumer Goods: Zinc Dies also play a significant role in the production of consumer goods, including jewelry and decorative items. The ability to replicate intricate designs allows for creative and innovative product offerings.
Zamak Die Casting in Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber die casting is a highly efficient method for producing zinc alloy parts. In this process, molten zinc alloy is injected into the die under high pressure, ensuring quick, detailed production. The low melting point of zinc makes it ideal for this technique, as it reduces wear on machinery and speeds up production.
Benefits of Hot Chamber Die Casting:
Faster Production: Rapid cycles for high-volume output.
Precision: Produces detailed, smooth parts with accuracy.
Durability: Zinc’s low melting point minimizes wear on equipment.
Cost-Efficient: Reduces material waste and energy consumption.
Consistency: Ensures uniform quality across production runs.
Complex Designs: Perfect for intricate shapes and detailed components.
Strong Properties: Excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
Case Studies and Examples
Zinc die casting presents distinct advantages for heat sink applications, particularly in terms of design flexibility and integrated construction.
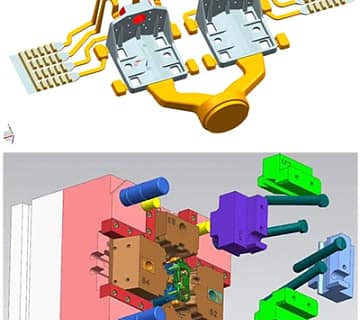
For instance, in the electronics industry, zinc molds enable the production of intricate heat sink enclosures and fins, enhancing device reliability. To demonstrate the practical application of these strategies, here’s a case study highlighting our approach to design and construction.

Zinc alloys, with their lower melting points and superior fluidity compared to aluminum, allow molten zinc to flow more easily into intricate mold designs. This includes thinner sections and complex geometries, making zinc ideal for producing highly detailed, precise parts with excellent surface finishes.
In heat sink applications, zinc die casting allows fins to be designed in any angle or shape, including complex forms like porcupine quills and airfoils. The process also integrates heat-dissipating fins directly into a single frame or enclosure, eliminating the need for additional components and assembly, which significantly reduces production costs.
Aluminum vs. Zinc Casting
While zinc is ideal for hot chamber machines due to its lower melting point, aluminium requires cold chamber machines, which have longer production cycles and increased equipment wear. Zinc casting offers faster production, shorter cooling times, and less strain on machinery compared to aluminium casting.
Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber Moulds
| Feature | Hot Chamber Mold | Cold Chamber Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Size & Design | Smaller, more compact molds; faster cycle times | Larger and more robust molds; designed to withstand higher injection pressure |
| Thermal Stress Resistance | Moderate, for materials with lower melting points like zinc | High, suitable for high-melting-point alloys like aluminum |
| Cooling System Requirements | Simpler cooling due to lower temperatures | More complex systems needed to manage heat |
| Mold Material | Standard tool steels (e.g., H13, P20) | High-grade steels with better heat resistance |
| Gate and Runner Design | Integrated with machine; smaller runners | Separate gating; larger runners for remote injection |
| Cycle Life | Longer due to less thermal/mechanical stress | Shorter unless properly cooled and maintained |
| Ejection System | Simpler and faster | More robust for larger parts and higher forces |
Environmental Impact
Zinc die casting aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing. Zinc is fully recyclable, promoting a closed-loop production cycle that reduces waste. The high precision of zinc casting also reduces the need for secondary processing, conserving energy and resources.
For more information on zinc die casting components or to explore custom solutions, contact DSW at sales@dswmould.com or call +86 (574) 27861829. Let us help you unlock new possibilities with advanced zinc casting technologies.













No comment