Unlocking the Potential of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting is a highly versatile and cost-effective method for producing precision components. Compared to other die cast metals such as aluminum or magnesium, zinc offers several advantages.
Zinc alloy casting provides superior accuracy and dimensional stability, making it ideal for intricate and complex part geometries. This precision translates into lower tooling costs, as the moulds used for zinc die casting can be less complex and expensive to produce.
Additionally, zinc alloy die casting offers a wide range of excellent physical and mechanical properties. Zinc alloys possess high strength, good hardness, and exceptional impact resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications. These alloys also exhibit excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, enhancing their performance in various industries.
Advantages of Zinc Casting
Cost Efficiency, Precision, and Versatility
Zinc offers several advantages when used in die casting, making it a preferred choice for various applications. One significant advantage is its ability to reduce tooling costs. Due to its low melting temperature, zinc allows for longer die life compared to aluminum and magnesium die casting. Dies used for zinc die casting can last up to 10 times longer than those used for aluminum and about five times longer than magnesium dies. This results in fewer repairs, less downtime, and increased part production throughout the tool’s lifespan.
Furthermore, for small zinc parts, the high-speed 4-slide miniature zinc die casting process can be utilized, significantly reducing upfront tooling costs compared to aluminum or magnesium. This process offers a cost-effective solution for producing zinc parts with complex geometries.
The advantages of zinc die casting include casting near net-shaped components with intricate geometries and thinner walls. Zinc castings require less draft angle and fewer machine features than other metals, reducing the need for post-processing and machining operations.
Zinc alloys exhibit an excellent balance of mechanical and physical properties. They have higher yield strength and elongation than aluminum or magnesium, enhancing durability and reliability. Zinc also possesses sound vibration dampening capacity, which is advantageous in applications where vibration control is essential.
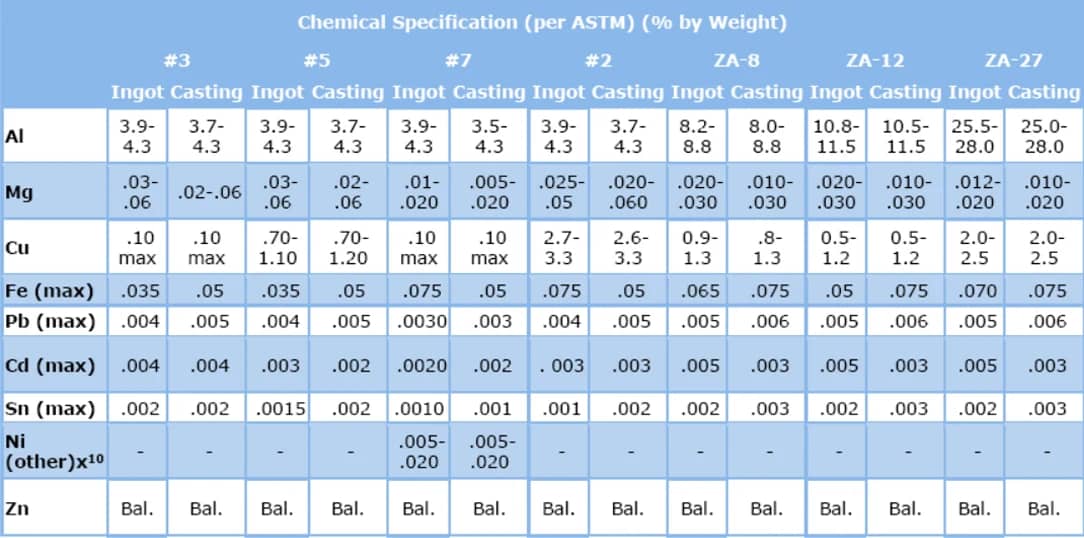
| Alloy | Zinc (Zn) | Aluminum (Al) | Magnesium (Mg) | Copper (Cu) | Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Tin (Sn) | Iron (Fe) | Nickel (Ni) |
| Zamak 2 | Balance | 3.9–4.3% | 0.02–0.05% | 2.7–3.3% | Max 0.003% | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
| Zamak 3 | Balance | 3.9–4.3% | 0.03% | Max 0.1% | Max 0.003% | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
| Zamak 5 | Balance | 3.9–4.3% | 0.02–0.05% | 0.75–1.25% | Max 0.003% | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
| Zamak 7 | Balance | 3.9–4.3% | 0.01–0.02% | Max 0.001% | Max 0.003% | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
| ZA-8 | Balance | 8.0–8.8% | 0.02–0.05% | 0.8–1.3% | – | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
| ZA-12 | Balance | 10.5–11.5% | 0.02–0.05% | 0.8–1.3% | – | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
| ZA-27 | Balance | 25–28% | 0.02–0.05% | 2.0–2.5% | – | Max 0.05% | Max 0.02% |
Zinc castings offer a wide range of finishing options. They can be easily plated, painted, or coated to achieve desired aesthetics, corrosion resistance, or other specific requirements.
Another advantage of zinc die casting is its faster production time. Zinc’s low melting temperature allows for quicker solidification and shorter cycle times, contributing to increased productivity and efficiency.
Rapid and Precise
Zinc Casting with Hot Chamber Process
Zinc casting utilizes the fast-cycling hot chamber process. Molten zinc is automatically injected into the die through a gooseneck. High pressure drives the metal into the die, rapidly solidifying within seconds. The part is then efficiently ejected from the tool. This process offers quick cycle times, precise dimensions, near-net-shape production, and excellent repeatability, making zinc die casting a cost-effective and efficient choice for various applications.
DSW specializes in casting zinc alloys, including Zamak No. 3, Zamak No. 5, and ZA-8. Zamak No. 3 is commonly used due to its superior castability and excellent finishing characteristics. It offers intricate detail, close dimensional tolerances, and the ability to be crimped or swaged. ZA-8 is chosen for applications requiring additional strength and greater creep resistance. With machine sizes up to 800 tons, DSW can produce zinc parts ranging from miniature to over 35 inches in length, catering to a wide range of customer needs.
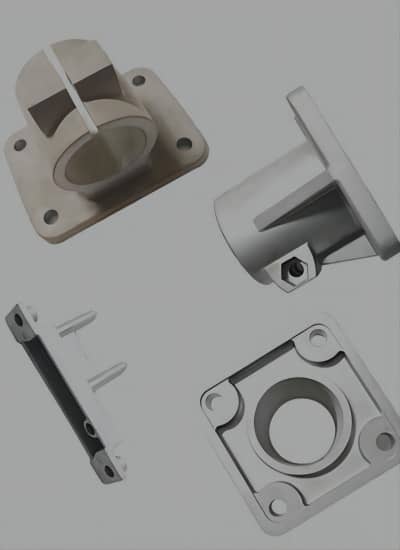
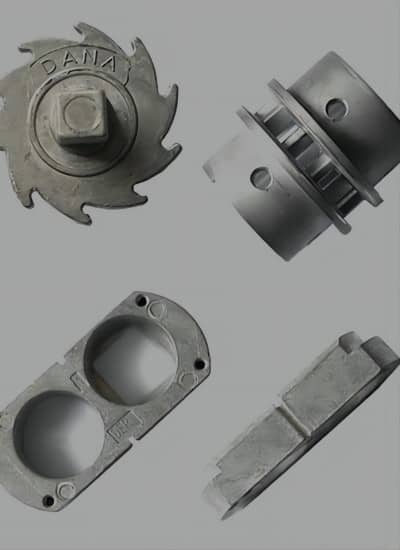
Common Components and Parts Made from Zinc Alloys
Zinc alloys play a vital role in manufacturing intricate, detailed components across a wide range of industries. Their exceptional casting properties, which allow for precise detail and tight dimensional tolerances, make zinc alloys highly effective for creating parts with thin walls and superior electrical performance. As the fourth most widely used metal globally, following iron, aluminum, and copper, zinc is indispensable in numerous industrial applications. Its most notable contribution is in the automotive industry, where zinc die casting technology was first developed and continues to thrive today.
Automotive Parts
Zinc die casting is extensively used in automotive manufacturing, particularly in hot chamber casting, which is known for its efficiency, high output, and ability to produce components with exact tolerances. Zinc offers cost savings over aluminum, and tools used in zinc die casting typically last longer, adding to the overall efficiency of the production process.
Key automotive components made through zinc die casting include:
- Gears and Pulleys: Zinc is used to manufacture gears and pulleys for seat belts due to its durability, hardness, and mechanical strength. These components must withstand significant wear and tear, making zinc an ideal material choice.
- Door Locks: Zinc’s strength and ability to be formed into complex shapes make it perfect for manufacturing door locks, not just in automobiles but also in various industrial applications.
- Enclosures: In automobiles, zinc alloys are often used for enclosures that house airbags and electrical components. Zinc’s excellent surface quality and electrical conductivity provide the necessary protection for sensitive electronics.
- Rearview Mirror Frames: Zinc’s casting capabilities allow for the precise and durable frames used in rearview mirrors.
- Sunroofs and Windshield Wipers: Both of these components are exposed to the elements and require resistance to rust and corrosion. Zinc die casting provides the necessary protection to ensure their longevity.
- Chassis Parts, Brackets, and Transmission Parts: Zinc die casting is favored for stress-bearing parts that require both strength and hardness. Zinc’s impact resistance and ability to maintain structural integrity under heavy loads make it an excellent choice for these applications.
In addition to these benefits, zinc’s recyclability is an increasingly important factor, especially in modern automotive manufacturing, where sustainability and efficiency are critical. Zinc can be reused without losing its core properties, making it an environmentally friendly choice for manufacturers.
Medical Instruments
The precision required in medical instruments makes zinc die casting an attractive option for this industry. Medical devices must meet stringent clinical standards, be biocompatible, and maintain their functionality after frequent sterilization. Zinc alloys excel in all these areas, offering exceptional hardness, self-lubrication, and dimensional stability.
Zinc’s ability to form precise, detailed components makes it ideal for advanced medical instruments that require intricate designs, such as minimally invasive surgical tools and diagnostic equipment. Zinc’s shielding properties are also valuable in medical devices containing delicate electronics, preventing electromagnetic interference and ensuring accurate patient readings.
The use of zinc die castings in operating table gearboxes and other medical device enclosures ensures reliability, safety, and durability, even in challenging medical environments.
Zinc Alloy Locks
Locks made from zinc alloys benefit from the material’s castability, allowing manufacturers to create complex shapes, thin walls, and smooth surfaces. These characteristics, combined with zinc’s lower material cost, make it an ideal choice for producing affordable, high-quality locks.
Zinc alloy locks are highly customizable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential and commercial door hardware to more specialized security systems. Their resistance to corrosion and wear ensures long-lasting performance in various environments.
Electronics
In the electronics industry, zinc die castings are used to shield sensitive components from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which can disrupt electronic systems. Zinc’s versatility in casting enables it to be molded into a variety of shapes, making it adaptable to different electronic applications, including enclosures for computers, telecom equipment, and industrial controls.
Zinc’s capacity to absorb vibrations also helps protect delicate electronic components, ensuring reliability and extending the lifespan of devices in high-stress environments.
Heat Sinks
Zinc die cast heat sinks offer significant advantages over aluminum heat sinks, particularly in the formation of complex shapes. Zinc’s casting properties allow for the integration of cooling fins directly into the frame, reducing thermal resistance and enhancing heat dissipation.
Though zinc is heavier than aluminum, it offers superior dimensional stability and better shielding against EMI and RFI. These qualities make zinc heat sinks an excellent choice in applications where both thermal management and electronic shielding are required, such as in high-performance computing and telecommunications equipment.


Customized Zinc Die Castings
Zinc’s versatility and durability make it an ideal choice for custom die casting projects. Selecting the right zinc alloy is crucial for achieving optimal results. Each zinc alloy has unique properties, with some better suited for hot chamber die casting and others for cold chamber processes.
When deciding on the appropriate zinc alloy, factors such as density, copper content, and overall cost should be carefully considered. Consulting with zinc die casting experts can help manufacturers identify the best alloy and process for their specific project, ensuring efficiency and precision.
Zinc’s malleability allows for the creation of custom parts that meet precise design specifications. Its resistance to creep and durability over time make it the perfect choice for applications that require long-lasting performance in challenging conditions.
The Power of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that offers exceptional precision, dimensional accuracy, and a wide range of physical and mechanical properties. It is a preferred choice for many applications where lightweight, durable, and intricately designed components are required.














No comment